LIMS is an important component for wet labs’ operations. Different from other physical components of the lab, LIMS can have more deployment options. It can be set up on the lab’s on-premises infrastructure or remotely in the cloud. With the growth of cloud technology and acceptance from public, cloud deployment becomes more popular. There are even multi-tenant LIMS systems now running in the cloud, which allows multiple labs to use the same system. But for serious labs, they will still prefer having a dedicated LIMS setup to fulfill the requirements for deep customization.
On-premises deployment
In lab operations, LIMS needs to interact with other lab systems, such as printer, QC and other equipment. On-premises LIMS deployment allows LIMS to reach them through direct network connection. Although sometimes, the network in the lab is segregated into different subnets, LIMS on one subnet can still reach equipment on others through defining specific network routing rule.
Another advantage of on-premises deployment is that it is easier to satisfy regulation requirements. LIMS run on the lab’s local IT infrastructure can be applied with the same IT policy regarding to access control, security and data management. It is easy to convince auditors that the lab’s IT setup applies same to all information systems during the lab certification process.
But the disadvantages of on-premises deployment are also obvious. Labs need to have strong local IT supports to deal with server setup, network configuration and data backup. For the labs with limited IT resource, there are extra costs associated with LIMS deployment and maintenance.
Cloud deployment
In cloud deployment model, the LIMS is set up on the virtual machine running in the lab controlled Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Security groups and policies are set up by the lab allowing the lab to access LIMS on the lab’s local computers. The security policy can be tailored to a very strict level. For example, only the permitted IPs (white-listed IPs) are allowed to access the LIMS’ server. The outbound network traffic from LIMS server can be limited also through security policy rules.
Deploying LIMS to the cloud also allows lab to take advantage of other benefits offered by the cloud platform. For example:
- Control the LIMS server’s online time. When the lab is not in operation, the server can be released to save cost. Scheduled LIMS running can be set up to align with lab’s operation time
- Automatic data backup. Data backup on the database used by the LIMS can be set up easily and without storage limitation
- Connection with computation resource. LIMS in the cloud can access the same resources as those for dry lab operation. If need, LIMS can even initiate computation intensive jobs in the cloud
However, LIMS deployed in the cloud still need to communicate with lab’s local equipment. And the communication is generally required for two-way directions. There are two solutions for it. One is through network peering and the other uses a dedicated LIMS agent running on-premises to handle the connection.
Connect LIMS in cloud with lab’s local resource
Network peering is the setup connecting lab’s local network with its VPC in cloud. For example, lab can set up IPsec VPN on the lab’s network switch for this purpose. After it is configured, network traffic between local network and VPC is encrypted and, although it still hits internet, is generally regarded safe. Cloud platform companies also provide other mechanisms for network peering allowing network traffic to totally avoid public internet.
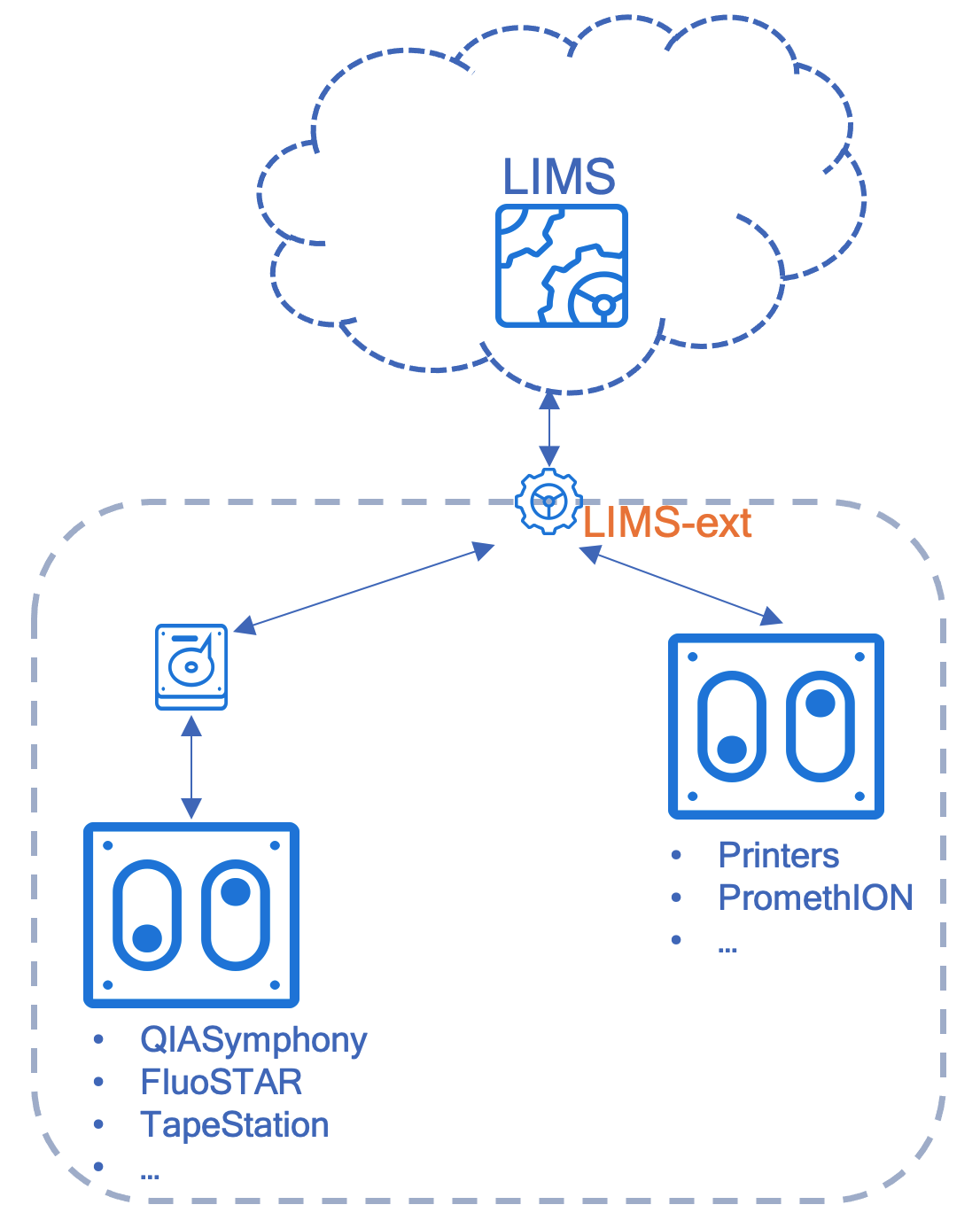
Another simpler solution is using a dedicated LIMS agent running on the lab’s local network. For example, SciTechLink has developed the LIMS-ext system for this purpose. It is a server running locally but is configured with two-way communication with LIMS. The LIMS-ext serves as the middle-man between LIMS and lab’s local equipment. It does not have local database to run and therefore, minimizes the requirements for local IT supports. LIMS-ext provides an extensible set of SDK (Software Development Kit) functions allowing LIMS to leverage. It also encapsulates the functions of working with lab’s local equipment, relieving the development efforts from LIMS end. By using LIMS deployed in cloud and LIMS-ext deployed on-premises, labs can benefit from both worlds.